Chasing CO₂ - one molecule at a time
10.11.2023
Rising levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are a threat to our civilisation. But it is really just a matter of small chemical building blocks, which are leftovers from various processes that make our modern society run. With CCS, we chase the most renown greenhouse gas - one molecule at a time.
Capturing and storing carbon dioxide will play an important role in achieving climate goals, alongside reducing the dependence on fossil fuels and investing in renewable energy sources. Industries and power plants will stop carbon dioxide from reaching the atmosphere where it contributes to rising temperatures. Sounds good - but how does this work?
Imagine a cloud of smoke rising from an industrial chimney.
“Today, this smoke is already purified from various types of particles and substances. But the smoke also contains carbon dioxide. CCS is about adding a step to the purification process and removing carbon dioxide from the smoke," says Anna Berggren, senior market- and sustainability director COWI in Sweden.
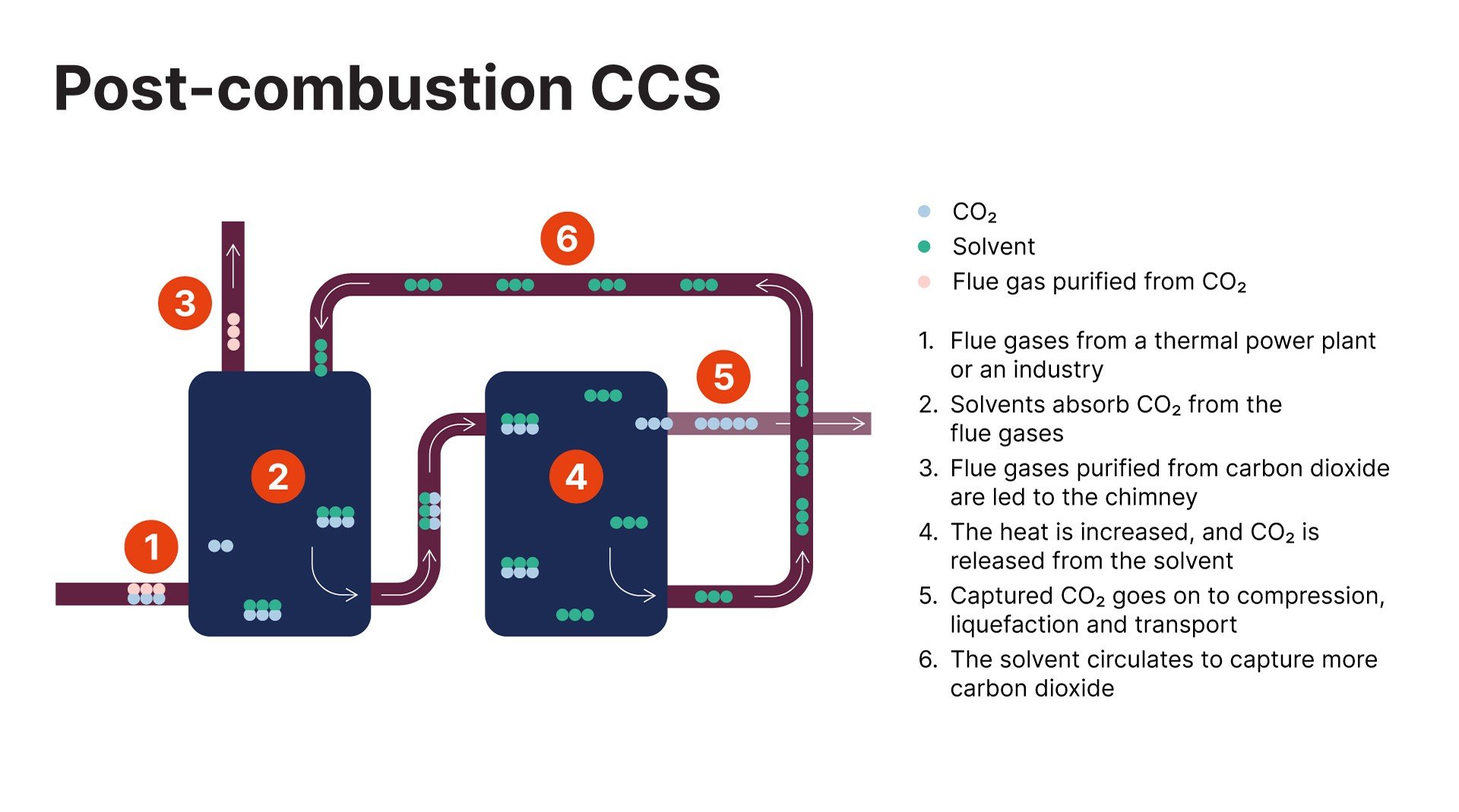
There are different processes for capturing carbon dioxide. We will focus on what is called "post-combustion CCS." Here, carbon dioxide molecules are collected from the smoke that comes when a raw material, either biogenic or fossil, is burned.
Let us describe post-combustion CCS in steps, at molecular level, in an industry where carbon dioxide is produced.
- The smoke is pressurised and directed into the bottom of a tower where it meets a solvent.
- This solvent can collect carbon dioxide molecules from the smoke, which then exits at the top of the tower through a chimney, now free of CO2.
- The solvent with captured carbon dioxide goes to another tower where the temperature is raised. The solvent then releases the carbon dioxide molecules, which are now concentrated and in gaseous form.
So now that we have collected CO₂ - what do we do with it?
This requires sea transport where the carbon dioxide is stored in liquid form in thermos-like containers. As a liquid, it takes up several hundred times less space than a gas. There are also options where the captured carbon dioxide is used as a raw material for new fuels and products. This is called carbon capture and utilisation (CCU) and temporarily stores CO2 in new products.
How effective is the carbon capture process?
COWI is part of several CCS projects, and in a series of articles we delve deep into the subject with the help of Anna Berggren, senior market- and sustainability director at COWI in Sweden. The next instalment in this series describes the road to large-scale carbon capture.
Get in contact

Anna Berggren
Senior Market Director
Business Development, Sweden
Tel:
+46 108501574
anbg@cowi.com